Pioneers Who Shaped the Field of Psychology
Psychology was shaped by brilliant minds who dared to question and redefine human behavior. These experts left behind theories that still influence how we understand ourselves today. Here’s a look at ten figures who stand out as the most well-known in the field of psychology.
1. Sigmund Freud
Freud's theory of the unconscious mind suggested that unconscious thoughts and feelings influence behavior. To uncover these thoughts, he developed psychoanalysis, a method involving techniques like free association and dream analysis. While some of his ideas have been questioned, Freud’s work is commendable in the history of psychology.
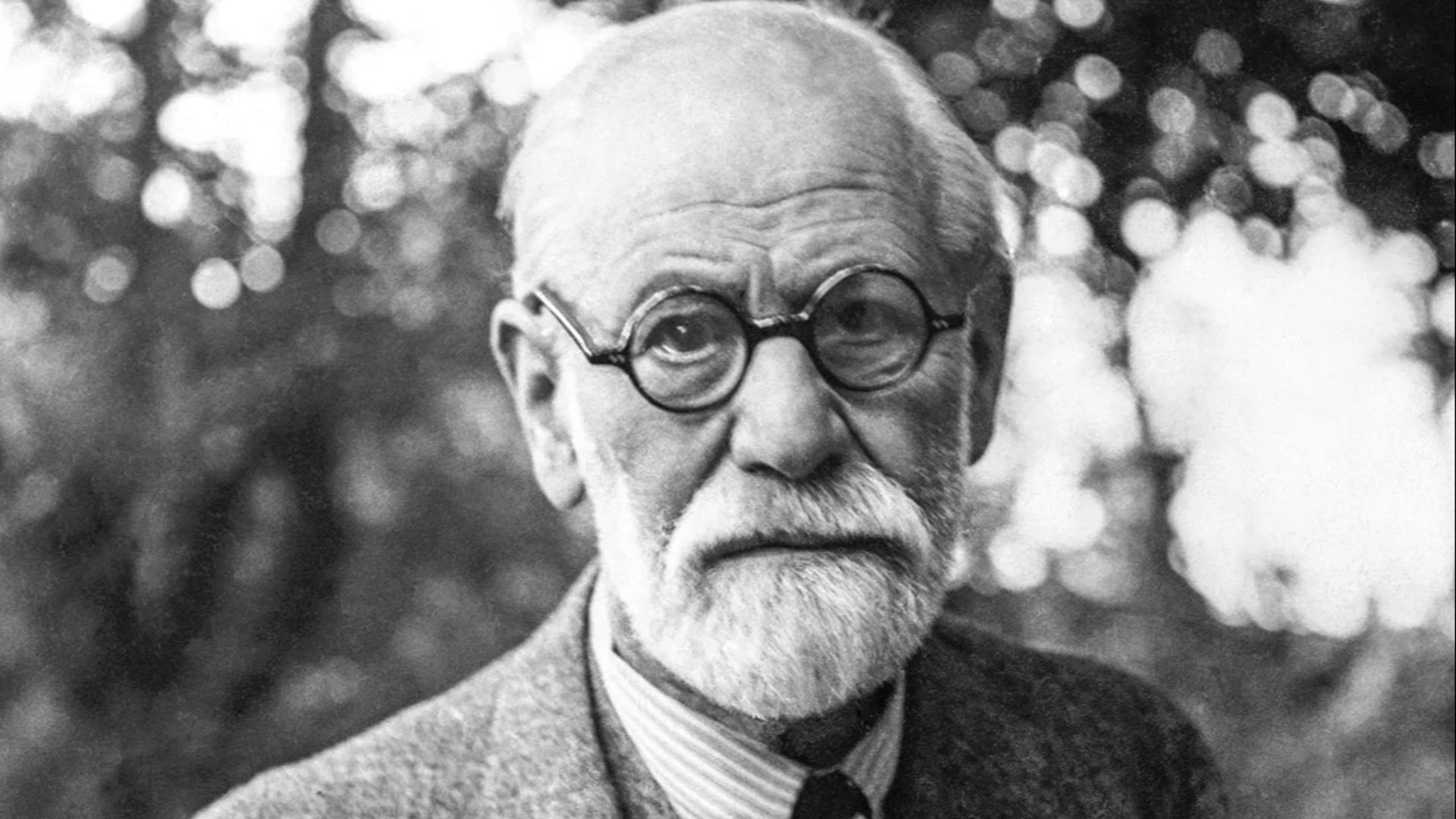 Paul De La Roussert on Wikimedia
Paul De La Roussert on Wikimedia
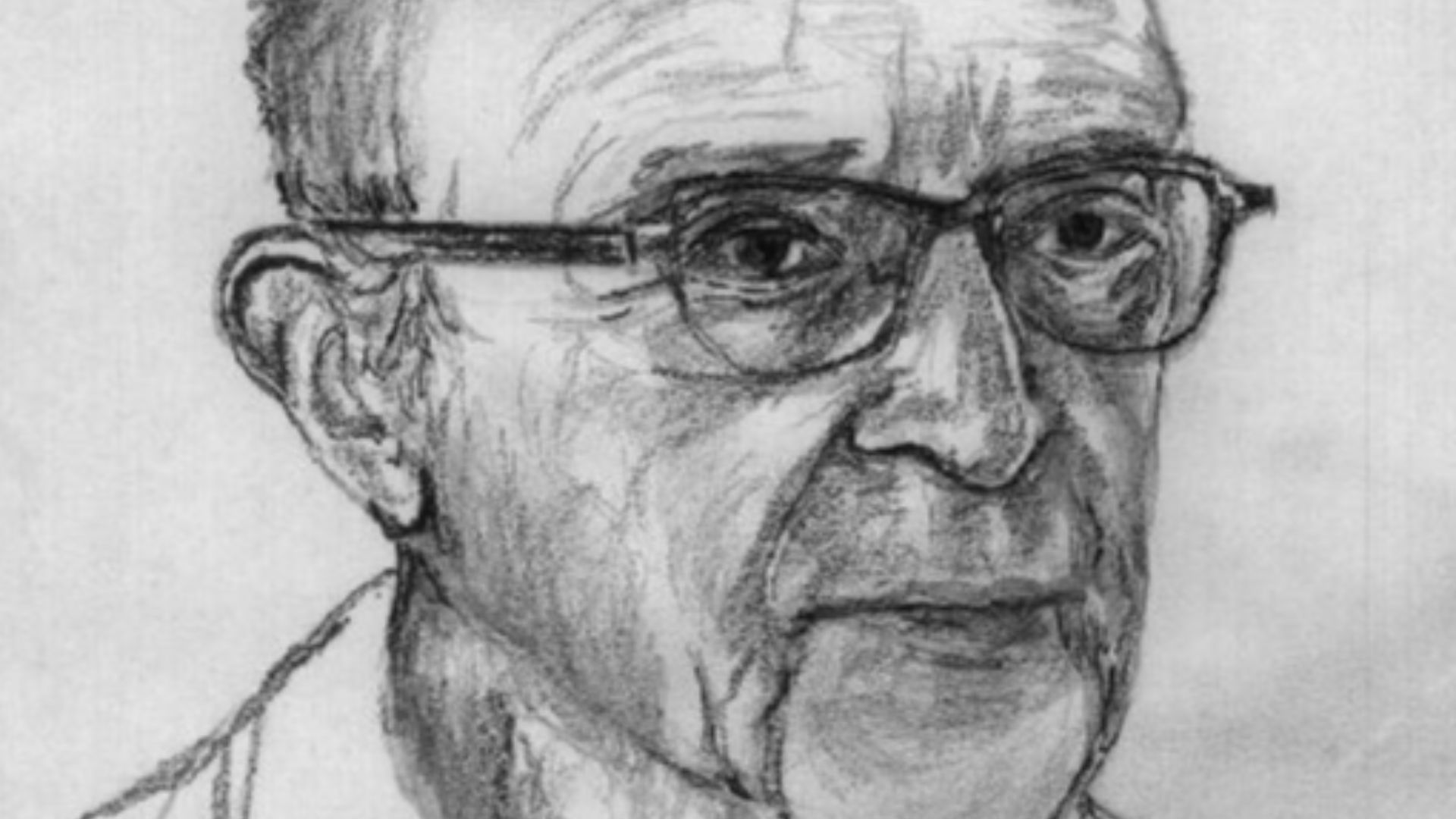
2. Carl Rogers
In the 1940s, Rogers created client-centered therapy by emphasizing the therapeutic relationship. His belief in unconditional positive regard helped clients explore their feelings in a non-judgmental space. Today, his ideas continue to shape modern therapeutic practices, including what we now call person-centered approaches.
 The original uploader was Didius at Dutch Wikipedia. on Wikimedia
The original uploader was Didius at Dutch Wikipedia. on Wikimedia
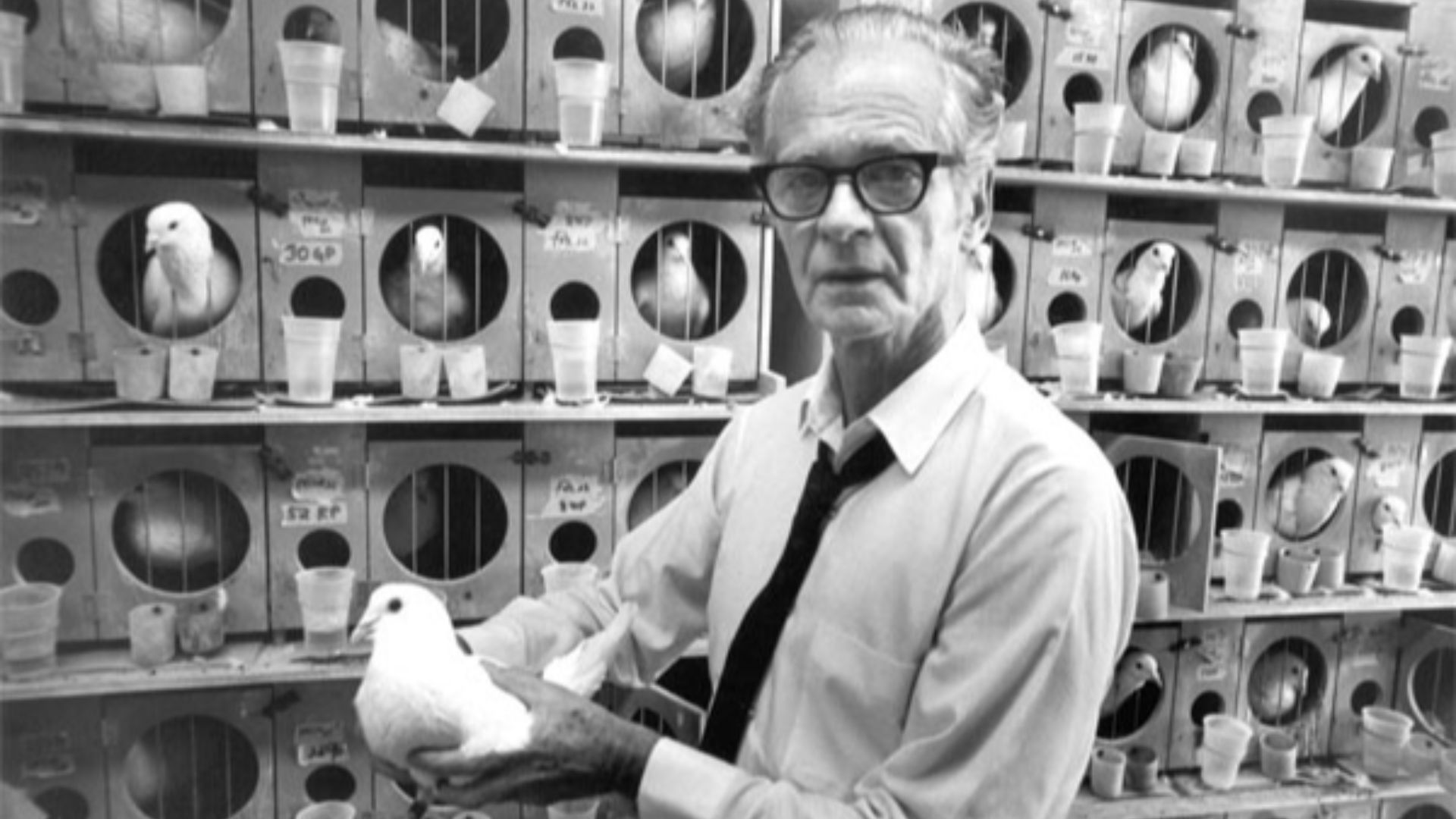
3. B.F. Skinner
Using reinforcement and punishment, Skinner demonstrated how behaviors could be strengthened or weakened. He influenced areas such as education, therapy, and even the design of environments to promote positive behaviors. Modern classrooms and mental health treatment have continuously improved since then.
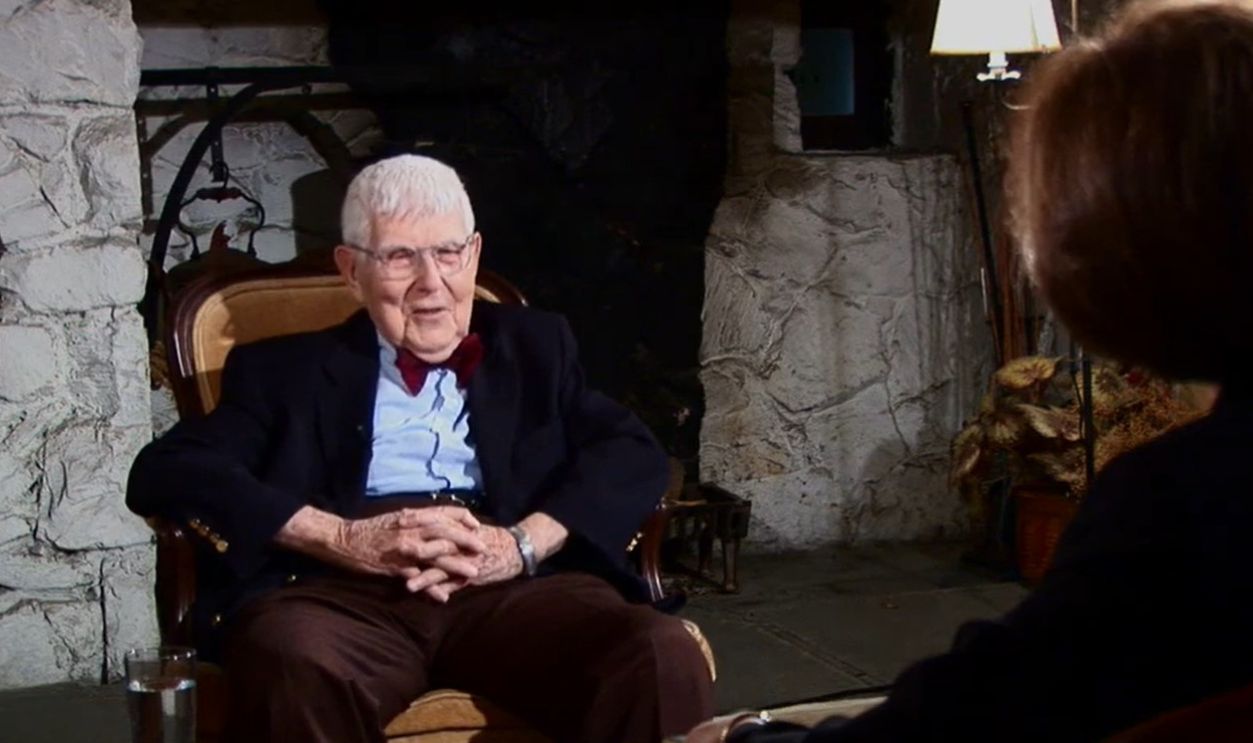
4. Aaron Beck
Beck’s cognitive therapy challenged traditional mental health treatments by focusing on how thoughts influence emotions. Back in the 1960s, he developed Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT), which targets negative thinking patterns. The result? CBT became a staple in treating everything.
 A Conversation with Aaron T. Beck by Annual Reviews
A Conversation with Aaron T. Beck by Annual Reviews
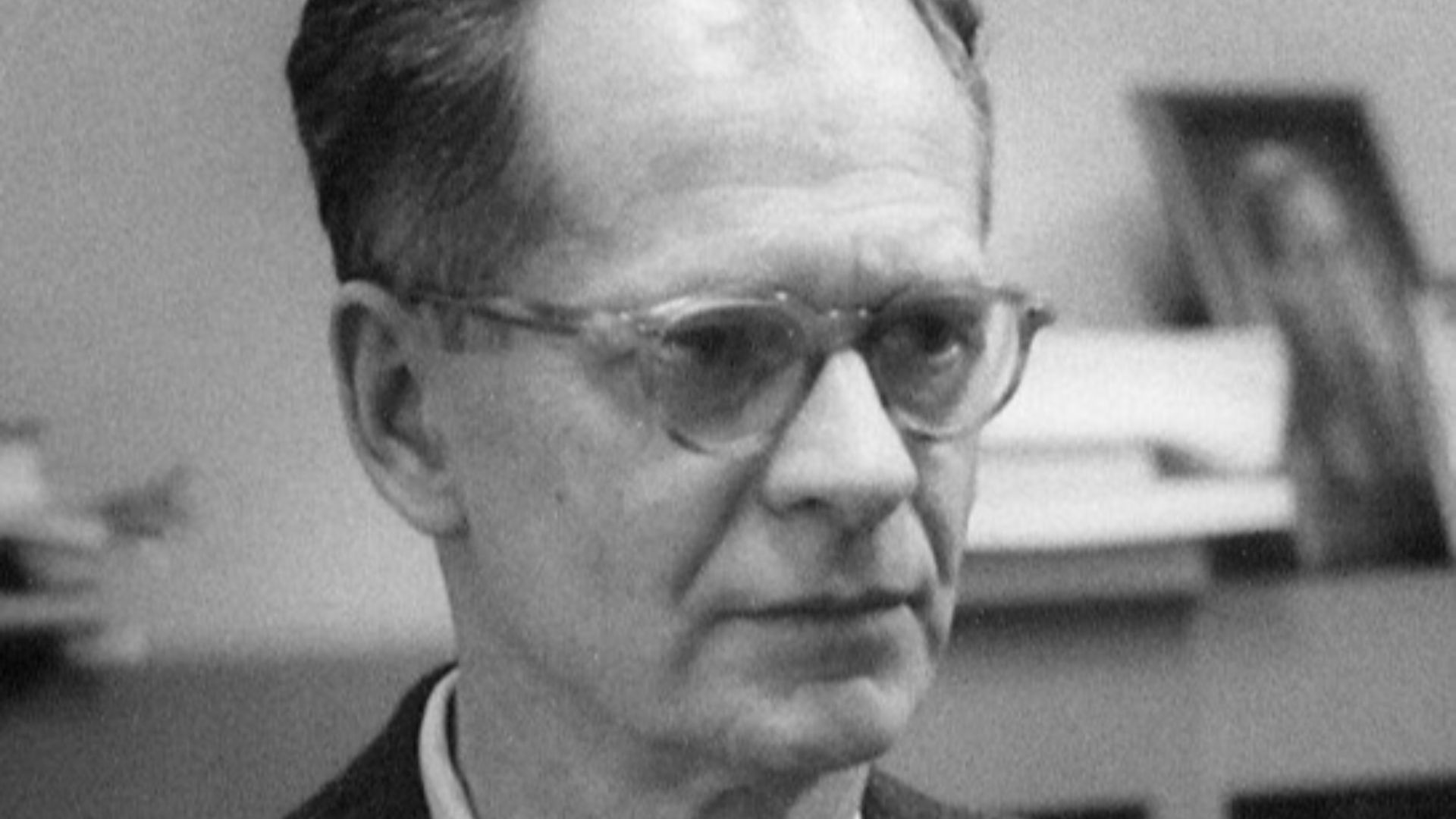
5. John B. Watson
Watson reasoned that psychology should be the science of behavior and objective observation, not introspection. To give weight to this approach, he conducted the famous “Little Albert” experiment and demonstrated how emotional responses could be conditioned in humans. He is now regarded as the father of behaviorism.
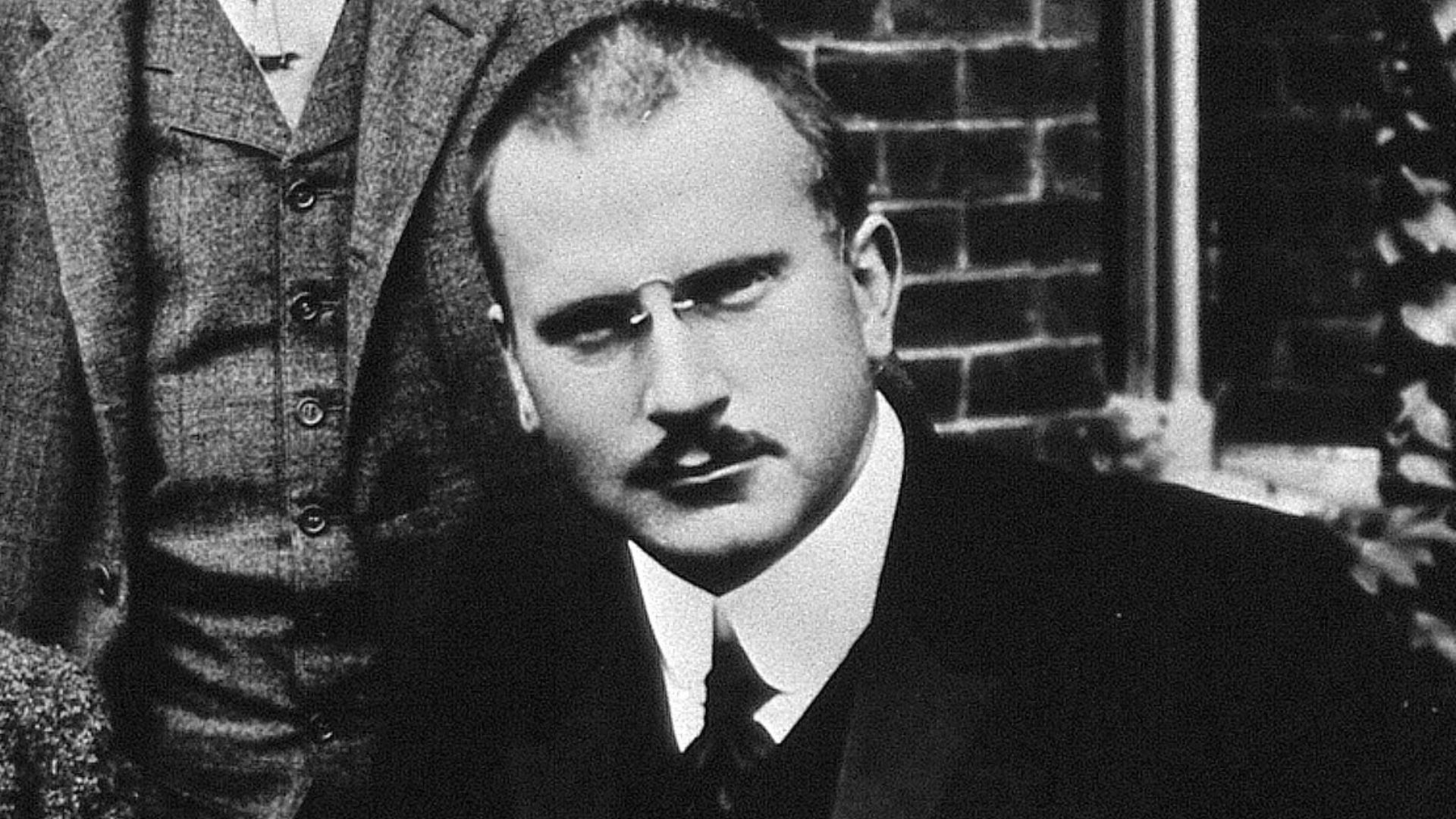
6. Carl Jung
Diverging from Freud’s views, Carl Jung took psychology into uncharted territory. His concept of the collective unconscious proposed that shared human experiences shape the psyche. Jung’s contributions bridged psychology with spirituality and continue to inspire fields beyond psychotherapy.
 Materialscientist on Wikimedia
Materialscientist on Wikimedia
7. Albert Bandura
Albert Bandura forever changed how we understand learning. By integrating cognition into behaviorism, Bandura developed social learning theory, which emphasized the importance of observational learning. Plus, his work has been applied in everything from media studies to parenting advice.
8. Abraham Maslow
At the heart of Maslow’s work lies his famous hierarchy of needs. This motivational theory, beginning with basic survival needs and culminating in self-actualization, highlights the human drive for growth and fulfillment. Unlike many of his contemporaries, Maslow focused on positive aspects of human behavior.
 Abraham Maslow - A Theory of Human Motivation (1943) by Essens Book Summaries
Abraham Maslow - A Theory of Human Motivation (1943) by Essens Book Summaries
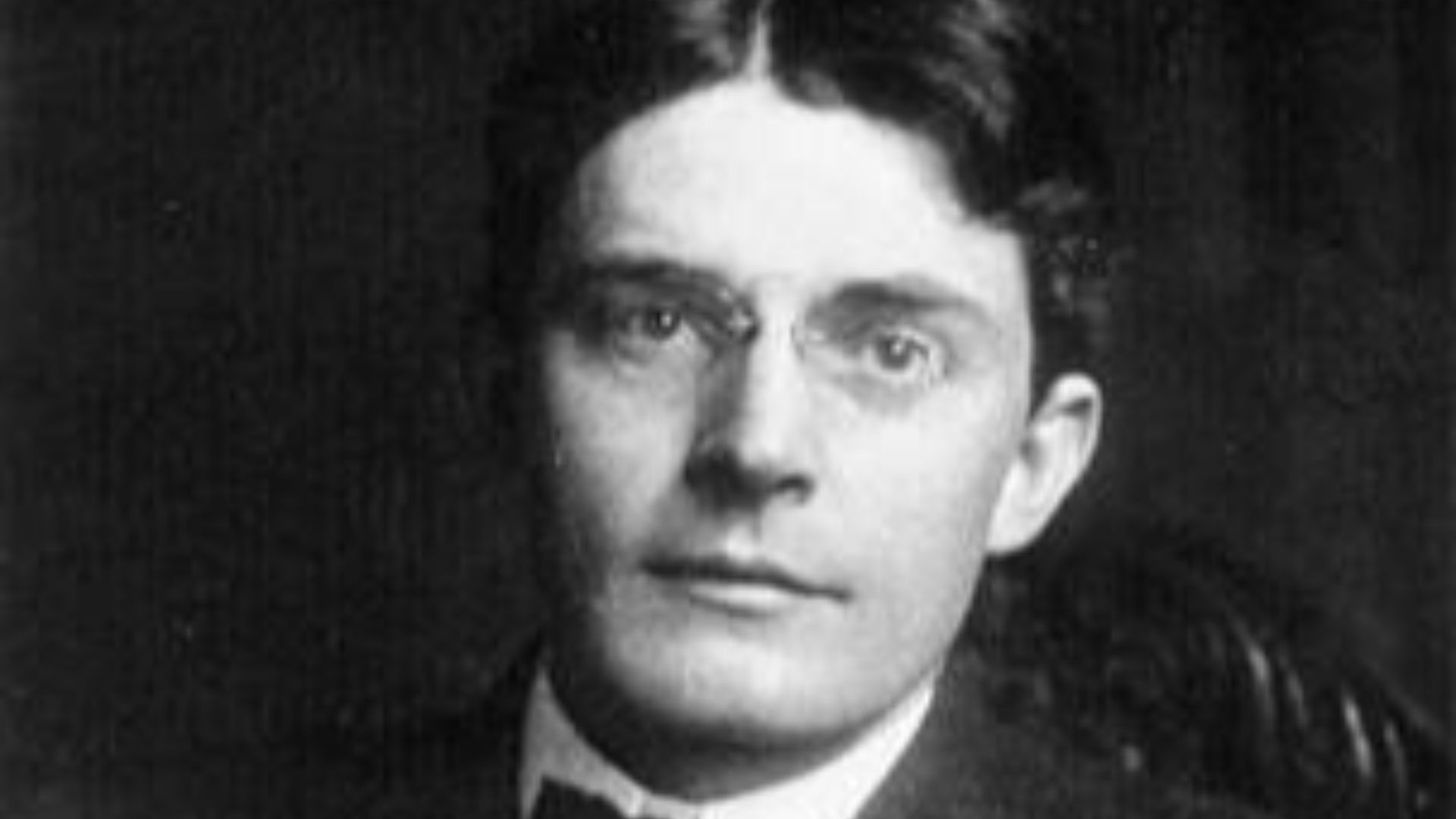
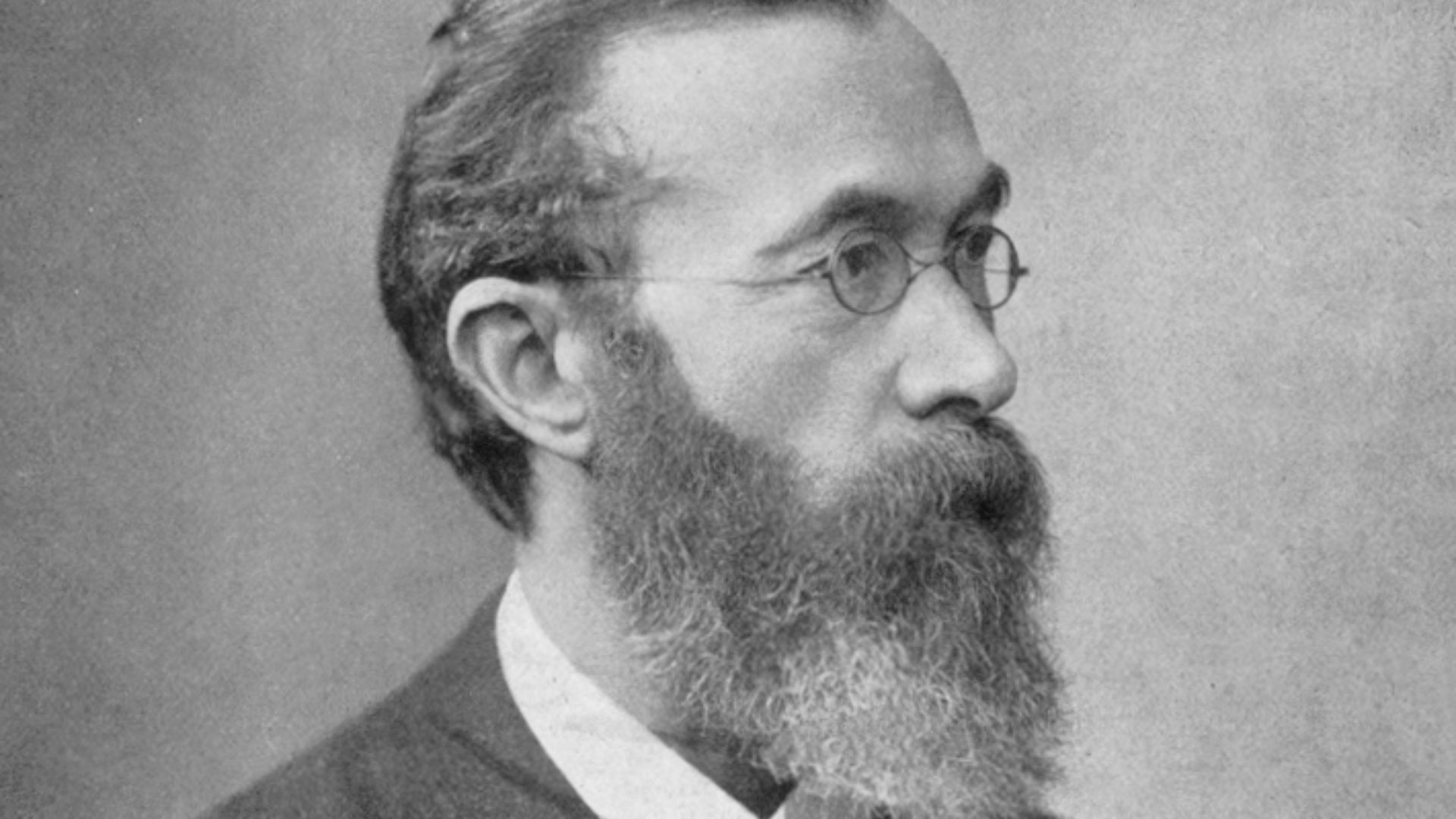
9. Wilhelm Wundt
Wundt’s legacy is rooted in his establishment of the first laboratory dedicated to psychological research. By using controlled experiments to study the mind, he helped transition psychology from philosophy to science. Today, he is celebrated as a pioneer of experimental methods in psychology.
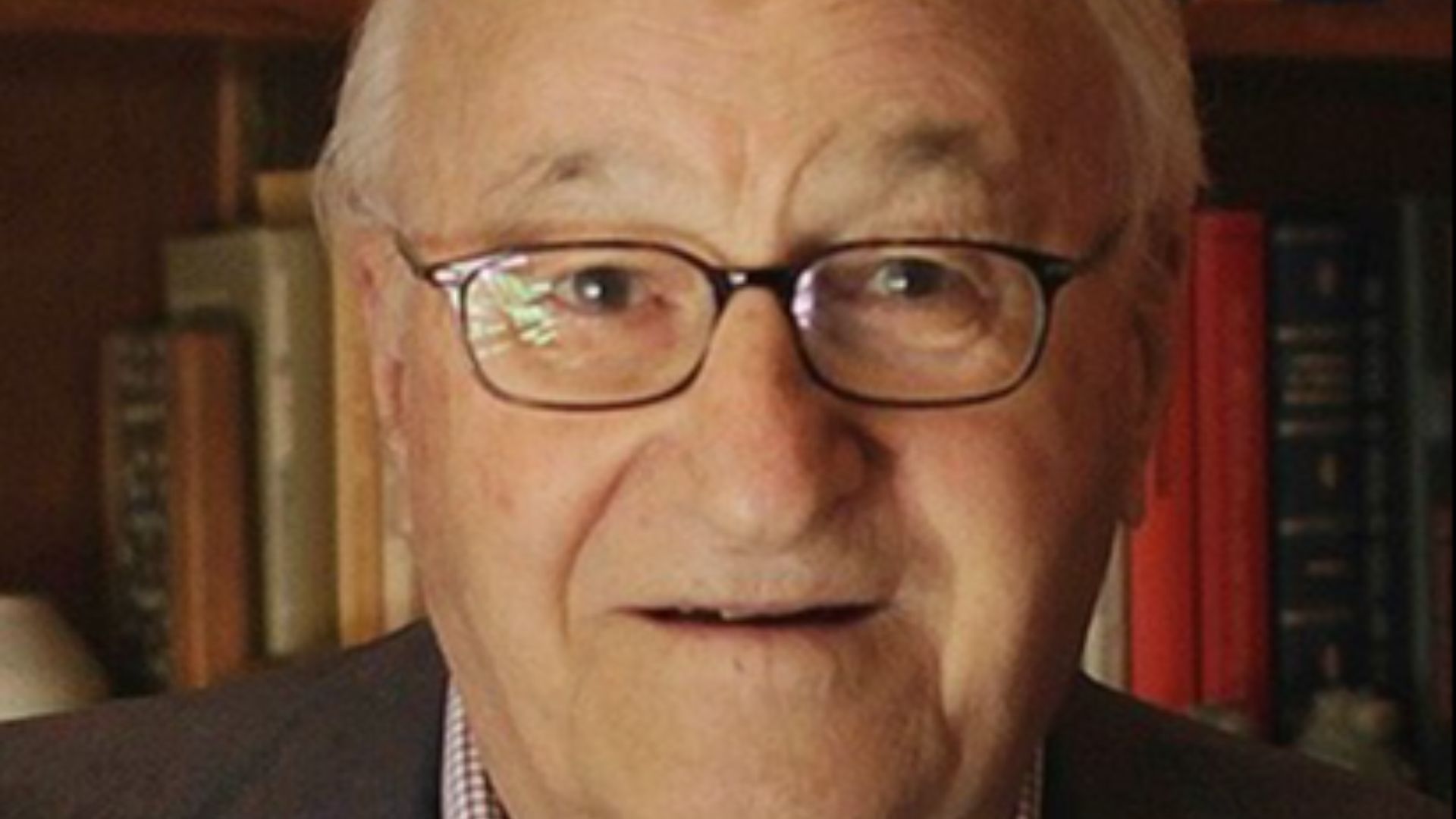
10. Erik Erikson
Erikson redefined how we think about human development. Erik's eight stages of psychosocial development illustrated the challenges individuals face throughout life. Erikson's theories offered a more holistic view of development. His work remains essential to understanding identity and life transitions.













